

CN 11-1911/B


Acta Psychologica Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (6): 745-758.doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2024.00745
• Reports of Empirical Studies • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Shunsen1, LAI Xiaoxiong1,2, ZHANG Cai3, ZHAO Xinmei1, DAI Xinran1, QI Mengdi1, WANG Huanlei1, WANG Wenrong4, WANG Yun1,*( )
)
Received:2023-04-10
Published:2024-06-25
Online:2024-04-08
Contact:
WANG Yun
E-mail:wangyun@bnu.edu.cn
Supported by:HUANG Shunsen, LAI Xiaoxiong, ZHANG Cai, ZHAO Xinmei, DAI Xinran, QI Mengdi, WANG Huanlei, WANG Wenrong, WANG Yun. (2024). Relationship between adolescents’ smartphone stress and mental health: Based on the multiverse-style analysis and intensive longitudinal method. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 56(6), 745-758.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://journal.psych.ac.cn/acps/EN/10.3724/SP.J.1041.2024.00745
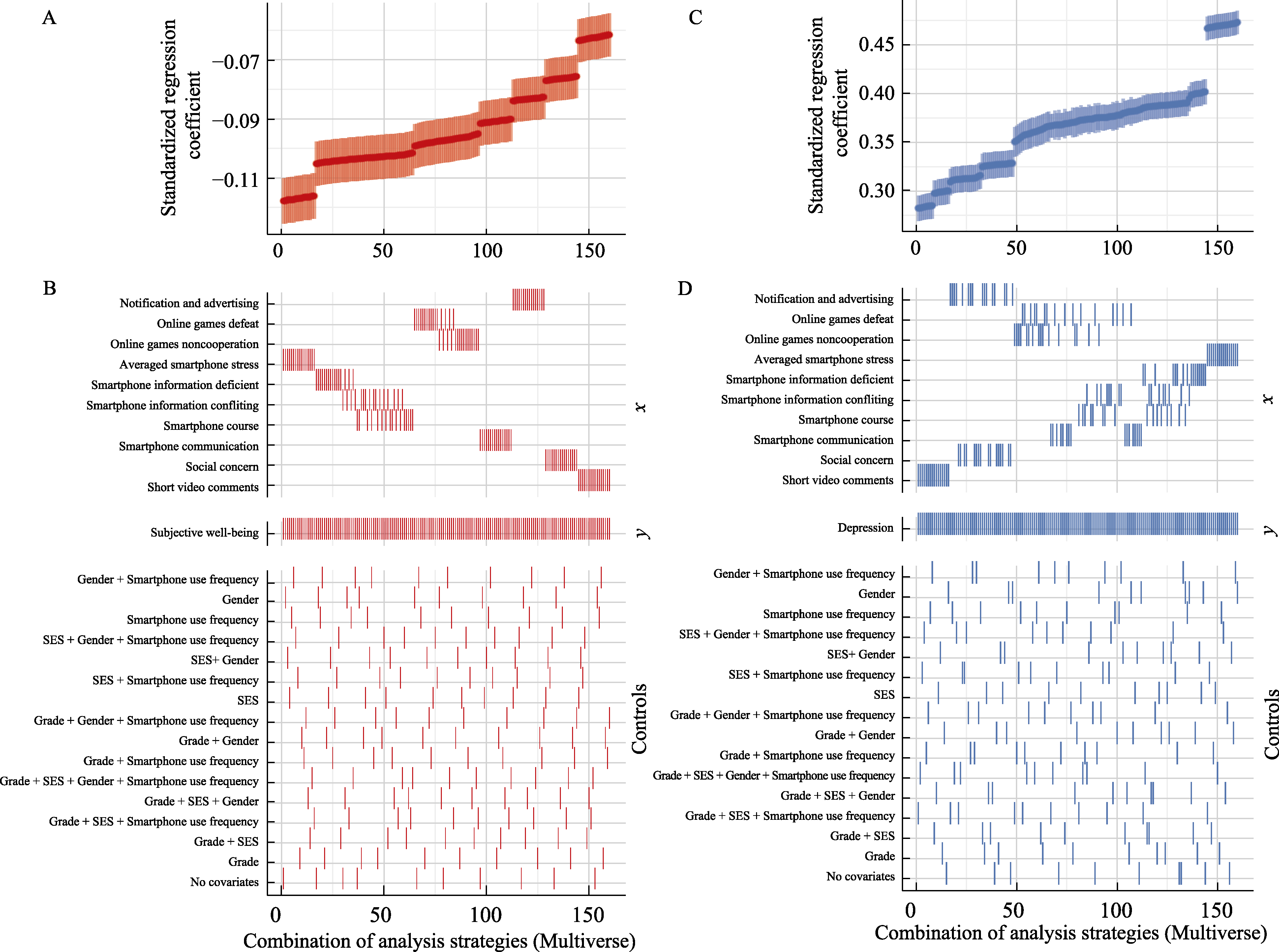
Figure 2. Strategy combinations of multiverse-style analysis and its curve. Note. The vertical coordinates of the points on the curve in Figure 2(A/C) represent the regression coefficients of the independent variable on the dependent variable under different strategy combinations, and the shaded area represents the confidence interval of this coefficient. On the right side of Figure 2(B/D), “controls” refers to control variables, “y” refers to the dependent variable, and “x” refers to the independent variable. Both red and blue indicate significant strategy combinations. Color figures are available in the electronic version.
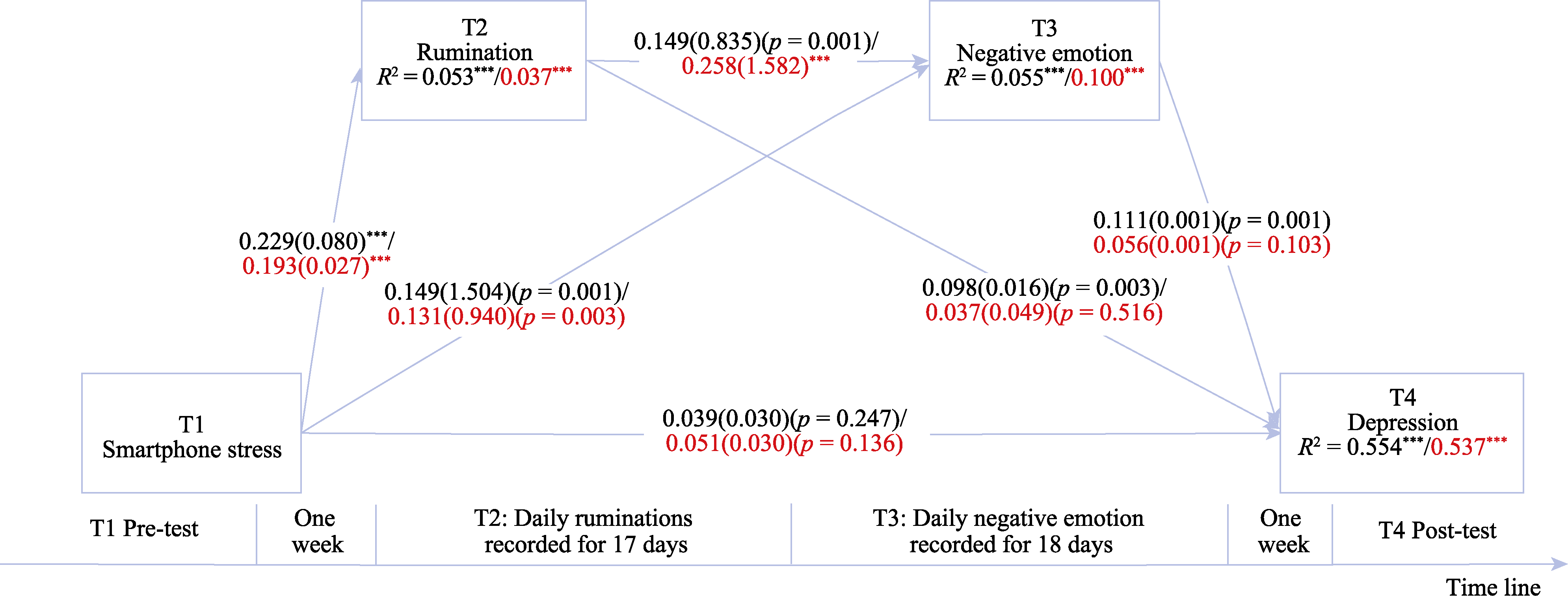
Figure 3. The Mediating Mechanism of Smartphone Stress on Adolescent Depression. Note. The coefficients in the figure are standardized coefficients. The black values represent the model coefficients and fitting when the mediating variable is intensity, and the values after the slash (bolded part) represent the model coefficients and fitting when the mediating variable is fluctuation.***p < 0.001.
| Model | Types of mediators | Paths | standardized effect | SE | 95% CI | Indirect effect size (PM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smartphone stress→ depression | Intensity | Total effect | 0.072 | 0.034 | 0.005 ~ 0.138 | NA |
| Total indirect effect | 0.043 | 0.012 | 0.020 ~ 0.069 | 59.72% | ||
| Smartphone stress-rumination-depression | 0.022 | 0.009 | 0.007 ~ 0.042 | 30.56% | ||
| Smartphone stress-negative emotion-depression | 0.017 | 0.008 | 0.004~ 0.035 | 23.61% | ||
| Smartphone-rumination-negative emotion-depression | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.0004 ~ 0.009 | 5.56% | ||
| Fluctuation | Total effect | 0.058 | 0.034 | ?0.008 ~ 0.124 | NA | |
| Total indirect effect | 0.014 | 0.010 | ?0.004 ~ 0.034 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress-rumination-depression | 0.004 | 0.009 | ?0.014 ~ 0.021 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress-negative emotion-depression | 0.007 | 0.006 | ?0.003 ~ 0.020 | NA | ||
| Smartphone-rumination-negative emotion-depression | 0.003 | 0.002 | ?0.001 ~ 0.008 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress→ wellbeing | Intensity | Total effect | ?0.067 | 0.192 | ?0.711 ~ 0.048 | NA |
| Total indirect effect | ?0.017 | 0.015 | ?0.048 ~ 0.011 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress-rumination-wellbeing | 0.015 | 0.009 | ?0.0004 ~ 0.034 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress-negative emotion-wellbeing | ?0.026 | 0.011 | ?0.052 ~ ?0.008 | 38.81% | ||
| Smartphone-rumination-negative emotion-wellbeing | ?0.006 | 0.003 | ?0.013 ~ ?0.001 | 8.96% | ||
| Fluctuation | Total effect | ?0.053 | 0.188 | ?0.645 ~ 0.101 | NA | |
| Total indirect effect | ?0.008 | 0.0101 | ?0.029 ~ 0.011 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress-rumination-wellbeing | 0.007 | 0.008 | ?0.007 ~ 0.024 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress-negative emotion-wellbeing | ?0.011 | 0.007 | ?0.027 ~ ?0.001 | 20.75% | ||
| Smartphone-rumination-negative emotion-wellbeing | ?0.004 | 0.003 | ?0.011 ~ ?0.0003 | 7.55% |
Table 1 Summary Table of the Mediating Effects of Smartphone Stress on Mental Health
| Model | Types of mediators | Paths | standardized effect | SE | 95% CI | Indirect effect size (PM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smartphone stress→ depression | Intensity | Total effect | 0.072 | 0.034 | 0.005 ~ 0.138 | NA |
| Total indirect effect | 0.043 | 0.012 | 0.020 ~ 0.069 | 59.72% | ||
| Smartphone stress-rumination-depression | 0.022 | 0.009 | 0.007 ~ 0.042 | 30.56% | ||
| Smartphone stress-negative emotion-depression | 0.017 | 0.008 | 0.004~ 0.035 | 23.61% | ||
| Smartphone-rumination-negative emotion-depression | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.0004 ~ 0.009 | 5.56% | ||
| Fluctuation | Total effect | 0.058 | 0.034 | ?0.008 ~ 0.124 | NA | |
| Total indirect effect | 0.014 | 0.010 | ?0.004 ~ 0.034 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress-rumination-depression | 0.004 | 0.009 | ?0.014 ~ 0.021 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress-negative emotion-depression | 0.007 | 0.006 | ?0.003 ~ 0.020 | NA | ||
| Smartphone-rumination-negative emotion-depression | 0.003 | 0.002 | ?0.001 ~ 0.008 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress→ wellbeing | Intensity | Total effect | ?0.067 | 0.192 | ?0.711 ~ 0.048 | NA |
| Total indirect effect | ?0.017 | 0.015 | ?0.048 ~ 0.011 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress-rumination-wellbeing | 0.015 | 0.009 | ?0.0004 ~ 0.034 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress-negative emotion-wellbeing | ?0.026 | 0.011 | ?0.052 ~ ?0.008 | 38.81% | ||
| Smartphone-rumination-negative emotion-wellbeing | ?0.006 | 0.003 | ?0.013 ~ ?0.001 | 8.96% | ||
| Fluctuation | Total effect | ?0.053 | 0.188 | ?0.645 ~ 0.101 | NA | |
| Total indirect effect | ?0.008 | 0.0101 | ?0.029 ~ 0.011 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress-rumination-wellbeing | 0.007 | 0.008 | ?0.007 ~ 0.024 | NA | ||
| Smartphone stress-negative emotion-wellbeing | ?0.011 | 0.007 | ?0.027 ~ ?0.001 | 20.75% | ||
| Smartphone-rumination-negative emotion-wellbeing | ?0.004 | 0.003 | ?0.011 ~ ?0.0003 | 7.55% |
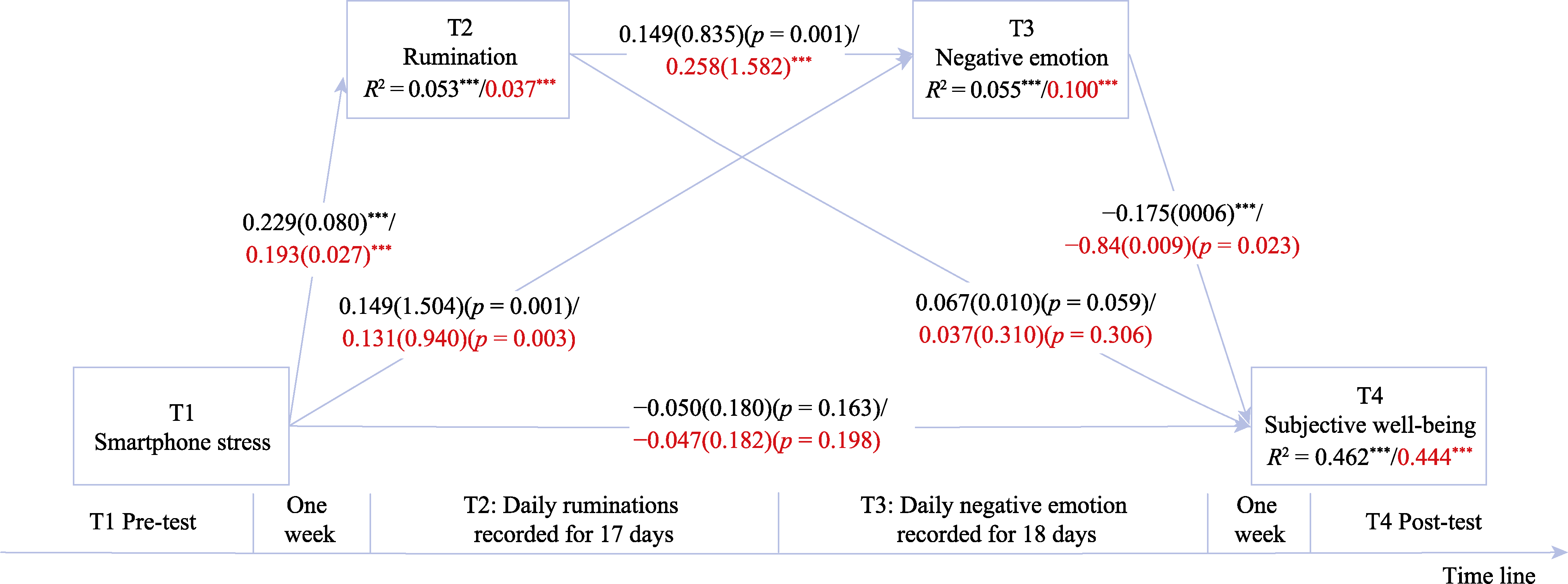
Figure 4. The Mediating Mechanism of Smartphone Stress on Adolescents Subjective Well-Being. Note. The coefficients in the figure are standardized coefficients. The black values represent the model coefficients and fitting when the mediating variable is intensity, and the values after the slash (bolded part) represent the model coefficients and fitting when the mediating variable is fluctuation. ***p < 0.001.
| Adolescent smartphone stress scale (short-version) | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| 1. Being unable to communicate clearly on my smartphone makes me anxious | Smartphone communication |
| 2. I feel irritated when I search out inconsistent content on my smartphone | Smartphone information conflicting |
| 3. I feel sad that I cannot find the information I want through my smartphone | Smartphone information deficient |
| 4. I feel angry when my teammates do not cooperate while playing mobile games | Online games noncooperation |
| 5. Losing mobile games makes me angry | Online games defeat |
| 6. Online classes’ failure to solve my study problems on the smartphone platform irritates me | Smartphone Course |
| 7. It makes me feel sad to see others insult, attack, or make mean comments about people I care about while browsing social media | Social concern |
| 8. The advertisements pushed to my mobile news feeds make me angry | Notifications and adverting |
| 9. Bad comments (e.g., abusive or offensive comments) in the comments section of short videos on my phone make me angry | Short video comments |
| Adolescent smartphone stress scale (short-version) | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| 1. Being unable to communicate clearly on my smartphone makes me anxious | Smartphone communication |
| 2. I feel irritated when I search out inconsistent content on my smartphone | Smartphone information conflicting |
| 3. I feel sad that I cannot find the information I want through my smartphone | Smartphone information deficient |
| 4. I feel angry when my teammates do not cooperate while playing mobile games | Online games noncooperation |
| 5. Losing mobile games makes me angry | Online games defeat |
| 6. Online classes’ failure to solve my study problems on the smartphone platform irritates me | Smartphone Course |
| 7. It makes me feel sad to see others insult, attack, or make mean comments about people I care about while browsing social media | Social concern |
| 8. The advertisements pushed to my mobile news feeds make me angry | Notifications and adverting |
| 9. Bad comments (e.g., abusive or offensive comments) in the comments section of short videos on my phone make me angry | Short video comments |
| [1] | Aarts, A. A., Anderson, J. E., Anderson, C. J., Attridge, P. R., Attwood, A., Axt, J., … Zuni, K. (2015). Estimating the reproducibility of psychological science. Science, 349(6251), aac4716. |
| [2] |
Agnew, R. (1992). Foundation for a general strain theory of crime and delinquency. Criminology, 30(1), 47-88.
doi: 10.1111/crim.1992.30.issue-1 URL |
| [3] | Andreas, J. B., & Brunborg, G. S. (2017). Depressive symptomatology among Norwegian adolescent boys and girls: The patient health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) psychometric properties and correlates. Frontiers in Psychology, 8(887), 1-11. |
| [4] |
Antaramian, S. P., Huebner, E. S., Hills, K. J., & Valois, R. F. (2010). A dual-factor model of mental health: Toward a more comprehensive understanding of youth functioning. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 80(4), 462-472.
doi: 10.1111/j.1939-0025.2010.01049.x URL |
| [5] |
Boer, M., Stevens, G. W. J. M., Finkenauer, C., & van den Eijnden, R. J. J. M. (2022). The complex association between social media use intensity and adolescent wellbeing: A longitudinal investigation of five factors that may affect the association. Computers in Human Behavior, 128, 107084.
doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2021.107084 URL |
| [6] | Bolger, N., & Laurenceau, J. -P. (2013). Intensive longitudinal Methods: An introduction to diary and experience sampling research. Guilford Press. |
| [7] | Chen, X., Ren, J., & Ma, T. (2009). The characters of positive mental health. Journal of Psychological Science, 32(2), 487-489. |
| [8] |
Choi, S. B., & Lim, M. S. (2016). Effects of social and technology overload on psychological well-being in young South Korean adults: The mediatory role of social network service addiction. Computers in Human Behavior, 61, 245-254.
doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.03.032 URL |
| [9] |
Cooke, P. J., Melchert, T. P., & Connor, K. (2016). Measuring well-being: A review of instruments. Counseling Psychologist, 44(5), 730-757.
doi: 10.1177/0011000016633507 URL |
| [10] |
Crone, E. A., & Konijn, E. A. (2018). Media use and brain development during adolescence. Nature Communications, 9(1), 1-10.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02088-w |
| [11] | Cui, L., & Zhang, G. (2005). A review of the research on positive psychology. Journal of Psychological Science, 28(2), 402-405. |
| [12] | Currie, C., Zanotti, C., Currie, D., Morgan, A., Currie, D., Looze, M. de, … Barnekow, V. (2012). Social determinants of health and well-being among young people. Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) study: International report from the 2009/2010 survey. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe. |
| [13] | CYLC, & CNNIC. (2022). Study on Internet use by minors nationwide in 2021. https://www.cnnic.net.cn/n4/2022/1201/c116-10690.html |
| [14] |
Daros, A. R., Daniel, K. E., Boukhechba, M., Chow, P. I., Barnes, L. E., & Teachman, B. A. (2020). Relationships between trait emotion dysregulation and emotional experiences in daily life: An experience sampling study. Cognition and Emotion, 34(4), 743-755.
doi: 10.1080/02699931.2019.1681364 URL |
| [15] |
Dawel, A., Gulliver, A., Farrer, L. M., Kalokerinos, E. K., Cherbuin, N., Calear, A. L., McCallum, S., Morse, A. R., & Monaghan, C. (2023). Do emotion intensity, variability, differentiation, co-occurrence, and positive-negative ratios make unique contributions to predicting longitudinal change in psychological distress and well-being? Emotion, 23(7), 1945-1959.
doi: 10.1037/emo0001204 pmid: 36633999 |
| [16] |
Dejonckheere, E., Mestdagh, M., Houben, M., Rutten, I., Sels, L., Kuppens, P., & Tuerlinckx, F. (2019). Complex affect dynamics add limited information to the prediction of psychological well-being. Nature Human Behaviour, 3(5), 478-491.
doi: 10.1038/s41562-019-0555-0 pmid: 30988484 |
| [17] | Dong, Q., & Lin, C. (Eds). (2011). Technical report of the national children’s study of China. Beijing: Science Press. |
| [18] |
Garnefski, N., Kraaij, V., & Spinhoven, P. (2001). Negative life events, cognitive emotion regulation and emotional problems. Personality and Individual Differences, 30(8), 1311-1327.
doi: 10.1016/S0191-8869(00)00113-6 URL |
| [19] |
Gruber, J., Kogan, A., Quoidbach, J., & Mauss, I. B. (2013). Happiness is best kept stable: Positive emotion variability is associated with poorer psychological health. Emotion, 13(1), 1-6.
doi: 10.1037/a0030262 pmid: 23163709 |
| [20] | Hall, J. A., Miller, A. J., & Christofferson, J. L. (Nov. 2021). Digital stress as a mediator of the association between mobile and social media use and psychological functioning. National Communication Association Conference in Seattle, WA, USA. |
| [21] |
Hall, J. A., Steele, R. G., Christofferson, J. L., & Mihailova, T. (2021). Development and initial evaluation of a multidimensional digital stress scale. Psychological Assessment, 33(3), 230-242.
doi: 10.1037/pas0000979 pmid: 33507798 |
| [22] |
Heady, B., Kelly, J., & Wearing, A. (1993). Dimensions of mental health: Life satisfaction, positive affect, anxiety and depression. Social Indicator Research, 29, 63-82.
doi: 10.1007/BF01136197 URL |
| [23] | Hefner, D., & Vorderer, P. (2017). Digital stress:Permanent connectedness and multitasking. In L.Reinecke & M. B.Oliver (Eds.), The Routledge handbook of media use and well-being: International perspectives on theory and research on positive media effects (pp. 237-249). Routledge. |
| [24] | Hosseinichimeh, N., Wittenborn, A. K., Rick, J., Jalali, M. S., & Rahmandad, H. (2018). Modeling and estimating the feedback mechanisms among depression, rumination, and stressors in adolescents. PLoS ONE, 13(9), 1-18. |
| [25] |
Huang, S., Chen, H., Lai, X., Dai, X., & Wang, Y. (2023). Multiverse-style analysis: Introduction and application. Advances in Psychological Science, 31(2), 196-208.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2023.00196 |
| [26] | Huang, S., Lai, X., Ke, L., Qin, X., Yan, J. J., Xie, Y., Dai, X., & Wang, Y. (2022). Smartphone stress: Concept, structure, and development of measurement among adolescents. Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace, 16(5), Article 1. |
| [27] | Huang, S., Lai, X., Li, Y., Cui, Y., & Wang, Y. (2023). Beyond screen time: The different longitudinal relations between adolescents’ smartphone use content and their mental health. Children, 10(5), 770. |
| [28] | Huang, S., Lai, X., Zhao, X., Dai, X., Yao, Y., Zhang, C., & Wang, Y. (2022). Beyond screen time: Exploring the associations between types of smartphone use content and adolescents’ social relationships. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(15), 8940. |
| [29] | Huang, S., Luo, Y., Lai, X., Jian, K., Xu, Z., & Wang, Y. (2022). Core symptoms of depression in chinese adolescents and comparison between different gender and levels of depression: A network analysis approach. Journal of Psychological Science, 45(5), 1115-1122. |
| [30] |
Jabutay, F. A., Suwandee, S., & Jabutay, J. A. (2022). Testing the stress‐strain‐outcome model in Philippines‐based call centers. Journal of Asia Business Studies, 17(2), 404-423.
doi: 10.1108/JABS-06-2021-0240 URL |
| [31] |
Keng, S. L., & Tong, E. M. W. (2016). Riding the tide of emotions with mindfulness: Mindfulness, affect dynamics, and the mediating role of coping. Emotion, 16(5), 706-718.
doi: 10.1037/emo0000165 URL |
| [32] |
Kircanski, K., Thompson, R. J., Sorenson, J., Sherdell, L., & Gotlib, I. H. (2018). The everyday dynamics of rumination and worry: precipitant events and affective consequences. Cognition and Emotion, 32(7), 1424-1436.
doi: 10.1080/02699931.2017.1278679 URL |
| [33] |
Koeske, G. F., & Koeske, R. D. (1993). A preliminary test of a stress-strain-outcome model for reconceptualizing the burnout phenomenon. Journal of Social Service Research, 17(3-4), 107-135.
doi: 10.1300/J079v17n03_06 URL |
| [34] |
Koster, E. H. W., De Lissnyder, E., Derakshan, N., & De Raedt, R. (2011). Understanding depressive rumination from a cognitive science perspective: The impaired disengagement hypothesis. Clinical Psychology Review, 31(1), 138-145.
doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2010.08.005 pmid: 20817334 |
| [35] |
Kuppens, P. (2015). It’s about time: A special section on affect dynamics. Emotion Review, 7(4), 297-300.
doi: 10.1177/1754073915590947 URL |
| [36] |
Kuppens, P., Van Mechelen, I., Nezlek, J. B., Dossche, D., & Timmermans, T. (2007). Individual differences in core affect variability and their relationship to personality and psychological adjustment. Emotion, 7(2), 262-274.
pmid: 17516805 |
| [37] | Lazarus, R. S. (1999). Stress and emotion: A new synthesis. Springer Publishing Company. |
| [38] | Li, J., Wang, W., & Shi, J. (2003). Positive psychology: A new trend in psychology. Advances in Psychological Science, 11(3), 321-327. |
| [39] | Li, Y., & Li, D. (2022). Research progress on related emotion regulation models of non-suicidal self-injury. Advances in Pyschology, 12(1), 246-252. |
| [40] |
Luqman, A., Masood, A., Shahzad, F., Shahbaz, M., & Feng, Y. (2021). Untangling the adverse effects of late-night usage of smartphone-based SNS among University students. Behaviour and Information Technology, 40(15), 1671-1687.
doi: 10.1080/0144929X.2020.1773538 URL |
| [41] | Ma, X., Ji, C., Chen, Q., & Shen, X. (2021). Effects of social media overloads on the civil servants task performance: A multiply mediation model. Public Administration and Policy Review, 5, 33-46. |
| [42] | Margolis, S., & Lyubomirsky, S. (2018). Cognitive outlooks and well-being. In E. Diener, S. Oishi, & L. Tay (Eds.), Handbook of well-being (pp. 1-26). UT: DEF Publishers. |
| [43] | Masur, P. K., & Scharkow, M. (2020). specr:Conducting and visualizing specification curve analyses (Version 0.2.1). R groups. https://masurp.github.io/specr/, https://github.com/masurp/specr |
| [44] |
Neumann, A., Van Lier, P. A. C., Frijns, T., Meeus, W., & Koot, H. M. (2011). Emotional dynamics in the development of early adolescent psychopathology: A one-year longitudinal study. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 39(5), 657-669.
doi: 10.1007/s10802-011-9509-3 pmid: 21494863 |
| [45] |
Nezlek, J. B. (2017). A practical guide to understanding reliability in studies of within-person variability. Journal of Research in Personality, 69, 149-155.
doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2016.06.020 URL |
| [46] |
Nick, E. A., Kilic, Z., Nesi, J., Telzer, E. H., Lindquist, K. A., & Prinstein, M. J. (2022). Adolescent digital stress: Frequencies, correlates, and longitudinal association with depressive symptoms. Journal of Adolescent Health, 70(2), 336-339.
doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2021.08.025 URL |
| [47] |
Nolen-Hoeksema, S., Wisco, B. E., & Lyubomirsky, S. (2008). Rethinking rumination. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 3(5), 400-424.
doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6924.2008.00088.x pmid: 26158958 |
| [48] | Odgers, C. L., & Jensen, M. R. (2020). Annual research review: Adolescent mental health in the digital age: facts, fears, and future directions. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 61(3), 336-348. |
| [49] |
Orben, A., & Przybylski, A. K. (2019). Screens, teens, and psychological well-being: Evidence From Three Time-Use-Diary Studies. Psychological Science, 30(5), 682-696.
doi: 10.1177/0956797619830329 pmid: 30939250 |
| [50] |
Orben, A., Przybylski, A. K., Blakemore, S. J., & Kievit, R. A. (2022). Windows of developmental sensitivity to social media. Nature Communications, 13(1), 1-10.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27699-2 |
| [51] | Pandey, R., & Choubey, A. K. (2010). Emotion and health: An overview. Journal of Projective Psychology and Mental Health, 17(2), 135-152. |
| [52] | Polnok, S., Auta, T. T., Santoso, H., Nugroho, W., Dalem, G., Mahajaya, G., … Mamoh, K. (2022). Statistics Kingdom:A very helpful basic statistical analysis tool for health students 413. Health Notions, 6(9), 413-420. |
| [53] |
Reinecke, L., Aufenanger, S., Beutel, M. E., Dreier, M., Quiring, O., Stark, B., Wölfling, K., & Müller, K. W. (2017). Digital stress over the life span: The effects of communication load and internet multitasking on perceived stress and psychological health impairments in a german probability sample. Media Psychology, 20(1), 90-115.
doi: 10.1080/15213269.2015.1121832 URL |
| [54] |
Schoemann, A. M., Boulton, A. J., & Short, S. D. (2017). Determining power and sample size for simple and complex mediation models. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 8(4), 379-386.
doi: 10.1177/1948550617715068 URL |
| [55] |
Scott, S. B., Ram, N., Smyth, J. M., Almeida, D. M., & Sliwinski, M. J. (2017). Age differences in negative emotional responses to daily stressors depend on time since event. Developmental Psychology, 53(1), 177-190.
doi: 10.1037/dev0000257 pmid: 28026195 |
| [56] |
Selby, E. A., Anestis, M. D., & Joiner, T. E. (2008). Understanding the relationship between emotional and behavioral dysregulation: Emotional cascades. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 46(5), 593-611.
doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2008.02.002 pmid: 18353278 |
| [57] |
Selby, E. A., Franklin, J., Carson-Wong, A., & Rizvi, S. L. (2013). Emotional cascades and self-injury: Investigating instability of rumination and negative emotion. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 69(12), 1213-1227.
doi: 10.1002/jclp.21966 pmid: 23381733 |
| [58] |
Selby, E. A., Kranzler, A., Panza, E., & Fehling, K. B. (2016). Bidirectional-compounding effects of rumination and negative emotion in predicting impulsive behavior: Implications for emotional cascades. Journal of Personality, 84(2), 139-153.
doi: 10.1111/jopy.12147 pmid: 25388298 |
| [59] |
Sheng, N., Yang, C., Han, L., & Jou, M. (2023). Too much overload and concerns: Antecedents of social media fatigue and the mediating role of emotional exhaustion. Computers in Human Behavior, 139, 107500.
doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2022.107500 URL |
| [60] | Staal, M. A. (2004). Stress, cognition, and human performance: A literature review and conceptual framework. National Aeronautics and Space Administration. |
| [61] |
Steele, R. G., Hall, J. A., & Christofferson, J. L. (2020). Conceptualizing digital stress in adolescents and young adults: Toward the development of an empirically based model. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 23(1), 15-26.
doi: 10.1007/s10567-019-00300-5 pmid: 31392451 |
| [62] | Stikkelbroek, Y., Bodden, D. H. M., Kleinjan, M., Reijnders, M., & Van Baar, A. L. (2016). Adolescent depression and negative life events, the mediating role of cognitive emotion regulation. PLoS ONE, 11(8), 1-16. |
| [63] |
Tarafdar, M., Maier, C., Laumer, S., & Weitzel, T. (2019). Explaining the link between technostress and technology addiction for social networking sites: A study of distraction as a coping behavior. Information Systems Journal, 30(1), 96-124.
doi: 10.1111/isj.v30.1 URL |
| [64] | Timm, C., Ubl, B., Zamoscik, V., Ebner-Priemer, U., Reinhard, I., Huffziger, S., Kirsch, P., & Kuehner, C. (2017). Cognitive and affective trait and state factors influencing the long-term symptom course in remitted depressed patients. PLoS ONE, 12(6), 1-16. |
| [65] | Tomczyk, S., & Hoferichter, F. (2022). Associations between social media use, psychological stress, well-being, and alpha-amylase levels in adolescents. Journal of Stress, Anxiety, Trauma, and Resilience, 1(20), 26-37. |
| [66] |
Twenge, J. M., Haidt, J., Lozano, J., & Cummins, K. M. (2022). Specification curve analysis shows that social media use is linked to poor mental health, especially among girls. Acta Psychologica, 224, 103512.
doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2022.103512 URL |
| [67] |
van Vugt, M. K., & van der Velde, M. (2018). How does rumination impact cognition? A first mechanistic model. Topics in Cognitive Science, 10(1), 175-191.
doi: 10.1111/tops.12318 pmid: 29383884 |
| [68] |
Walerius, D. M., Fogleman, N. D., & Rosen, P. J. (2016). The role of ADHD and negative emotional lability in predicting changes in parenting daily hassles. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 25(7), 2279-2291.
doi: 10.1007/s10826-016-0381-1 URL |
| [69] |
Weinstein, E. C., & Selman, R. L. (2016). Digital stress: Adolescents’ personal accounts. New Media and Society, 18(3), 391-409.
doi: 10.1177/1461444814543989 URL |
| [70] |
Wen, Z., Fan, X., Ye, B., & Chen, Y. (2016). Characteristics of an effect size and appropriateness of mediation effect size measures revisited. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(4), 435-443.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.00435 |
| [71] | Xia, H., Han, X., Cheng, J., Liu, D., Wu, Y., & Liu, Y. (2022). Effects of negative life events on depression in middle school students: The chain-mediating roles of rumination and perceived social support. Frontiers in Psychology, 13(August),1-10. |
| [72] |
Zheng, Y., Zhou, Z., Liu, Q., Yang, X., & Fan, C. (2019). Perceived stress and life satisfaction: A multiple mediation model of self-control and rumination. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 28(11), 3091-3097.
doi: 10.1007/s10826-019-01486-6 |
| [73] | Zhou, H., & Long, L. (2004). Statistical remedies for common method biases. Advances in Psychological Science, 12(6), 942-950. |
| [74] |
Zubin, J., & Spring, B. (1977). Vulnerability — A new view of schizophrenia. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 86(2), 103-126.
doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.86.2.103 pmid: 858828 |
| [1] | YUAN Hang, LUO Siyang. Representation similarity analysis − A new perspective to study sociocultural change: Taking the mental health of elderly people as an example* [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2024, 56(7): 938-953. |
| [2] | DONG Niannian, YIN Kui, XING Lu, SUN Xin, DONG Yanan. The effects of daily supervisor negative feedback on employee creativity [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(5): 831-843. |
| [3] | WANG Xiaoqin, TAN Yafei, MENG Jie, LIU Yuan, WEI Dongtao, YANG Wenjing, QIU Jiang. The influence of emotion regulation flexibility on negative emotions: Evidence from experience sampling [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(2): 192-209. |
| [4] | HU Yiqiu, ZENG Zihao, PENG Liyi, WANG Hongcai, LIU Shuangjin, YANG Qin, FANG Xiaoyi. The effects of the parent-child relationship and parental educational involvement on adolescent depression, self-injury, and suicidal ideation: The roles of defeat and meaning in life [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2023, 55(1): 129-141. |
| [5] | JIANG Yuan-Ping, JIANG Cheng-Ming, HU Tian-Yi, SUN Hong-Yue. Effects of emotion on intertemporal decision-making: Explanation from the single dimension priority model [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2022, 54(2): 122-140. |
| [6] | YANG Weiwen, LI Chaoping. The relationship between perceived overqualification and individual performance and mediating mechanisms: A meta-analytic review and examination of emotional and cognitive processing systems and cultural contexts [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(5): 527-554. |
| [7] | GE Xiaoyu, HOU Yubo. Confucian ideal personality traits (Junzi personality) and mental health: The serial mediating roles of self-control and authenticity [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(4): 374-386. |
| [8] | JIANG Guangrong, LI Danyang, REN Zhihong, YAN Yupeng, WU Xinchun, ZHU Xu, YU Lixia, XIA Mian, LI Fenglan, WEI Hui, ZHANG Yan, ZHAO Chunxiao, ZHANG Lin. The status quo and characteristics of Chinese mental health literacy [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2021, 53(2): 182-198. |
| [9] | REN Zhihong, ZHAO Chunxiao, TIAN Fan, YAN Yupeng, LI Danyang, ZHAO Ziyi, TAN Mengling, JIANG Guangrong. Meta-analysis of the effect of mental health literacy intervention in Chinese people [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(4): 497-512. |
| [10] | HAN Yichu, WEN Hengfu, CHENG Shuhua, ZHANG Chungan, LI Xin. Relationship between perceived discrimination and mental health of migrant children: A meta-analysis of Chinese students [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2020, 52(11): 1313-1326. |
| [11] | YANG Ruijuan, YOU Xuqun. Advancing the Effort-Reward Imbalance Model: Economic rewards influence on teachers’ mental health [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(9): 1184-1194. |
| [12] | LIAN Shuailei, SUN Xiaojun, NIU Gengfeng, ZHOU Zongkui. Upward social comparison on SNS and depression: A moderated mediation model and gender difference [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(7): 941-952. |
| [13] | ZHAO Mengxue; FENG Zhengzhi; WANG Yichao; LAI Wei; HU Feng; LIU Keyu; XIA Fan; JIANG Juan; WANG Jia; XIA Lei. Chinese military mental health at high altitude, 1993-2013: A cross-temporal meta-analysis of SCL-90 [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(5): 653-662. |
| [14] | LIU Qingqi, ZHOU Zongkui, NIU Gengfeng, Fan Cuiying. Mobile phone addiction and sleep quality in adolescents: Mediation and moderation analyses [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(12): 1524-1536. |
| [15] | HOU Lulu, JIANG Qi, WANG Huanzhen, LI Changran. The relationship between trait anger and aggressive behavior: Based on the perspective of the integrative cognitive model [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 2017, 49(12): 1548-1558. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||